 25 Sep 2021
25 Sep 2021
3 Primary Types of Arthritis
What is arthritis?
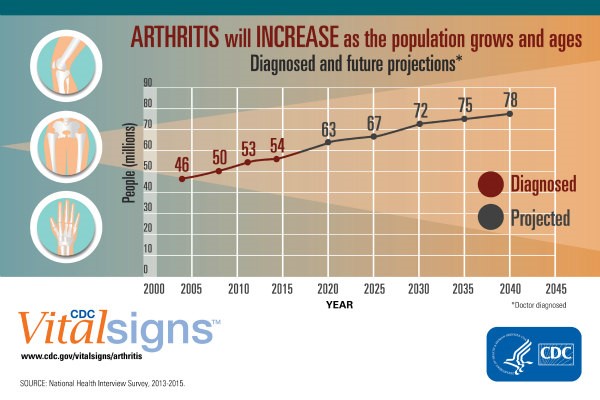
Arthritis is chronic inflammation of a joint, or multiple joints, which can cause deterioration of cartilage and other structural abnormalities over time such as bone spurs. Between 2013-2015, 54.4 million (22.7%) adults had physician-diagnosed arthritis, and 23.7 million had arthritis-attributable activity limitations. There are hundreds of different kinds of arthritis with various causes; the most common type is Osteoarthritis, followed by Rheumatoid Arthritis, and then Psoriatic Arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis (OA): According to the CDC, Osteoarthritis affects nearly 32.5 million US adults, and is one of the most expensive conditions to treat when joint replacement is required. Joints that weight bear are most commonly affected, such as knees, hips, spine, and feet. OA can be caused by anything that put excess stress or “wear and tear,” such as injuries, obesity, or age. A sedentary lifestyle can also be a risk factor for OA.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disease leading to inflammation of the joint lining causing pain, swelling, and stiffness which is often worse following rest. Wrists and hands are the most commonly affected areas, occurring symmetrically on both sides of the body. This type of arthritis can also cause overall fatigue and muscle weakness.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Psoriasis is another autoimmune disease initially presenting as a dry, flaky, red skin rash that can spread to the joints causing inflammation and swelling. Other symptoms include nail bed changes and general fatigue.
Diagnosis of Arthritis:
- Arthritis is diagnosed through a combination of X-ray imaging, pattern of stiffness of the affected joint with rest and activity, as well as decreased function and range of motion.
How can physical therapy and physical activity help treat arthritis?
- Addressing muscle imbalances and strengthening surrounding musculature can decrease the stress placed on the affected joint
- Manual therapy can improve range of motion, decrease swelling and pain using soft tissue massage, traction, and joint mobilizations
- Physical therapy can help to improve daily function, slow the progression of arthritis, as well as decrease the risk of arthritis in the future through preventative care.
- Regular physical activity is an important strategy for relieving pain and maintaining or improving function in people with arthritis
- Nearly half of adults with arthritis report no leisure time physical activity. Not being physically active is detrimental for arthritis and is a risk factor for other chronic diseases.
- Regardless of the type of arthritis you are diagnosed with, the physical therapists at Live to Move can help you achieve your goals for the future and desired level of function
References
- Barbour, K. E., Helmick, C. G., Boring, M., & Brady, T. J. (2014). Vital Signs: Prevalence of Doctor-Diagnosed Arthritis and Arthritis-Attributable Activity Limitation — United States, 2013–2015. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 66(9), 246-253. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6609e1
Arthritis Google trends: Diclofenac, Hydroxychloroquine, voltaren gel, nodule, hand pain, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, topical medication, immune system, are tomatoes bad for arthritis?, NIH worst foods for arthritis, compression gloves for arthritis, is arthritis an autoimmune, how is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed
News
COMMENTS: 1 Comment
6 Common Myths About Physical Therapy
- You need a referral to see a physical therapist.
False. Most people believe you need a referral to be evaluated by a physical therapist, which is not true. The state of Texas has direct access where you are able to see a doctor of physical therapy for evaluation and treatment within 10 business days before you need a physician to approve further care.
- Physical therapy is the same as massage.
False. While soft tissue massage may be part of your treatment plan, manual therapy performed by a physical therapist also includes joint mobilization and manipulation techniques. This is done prior to strengthening and therapeutic exercises that restore function to help you move with less pain.
- Physical therapy is only for injuries.
False. Physical therapy is used for more than just recovering from an injury through strengthening and stretching. Doctors of Physical Therapy also have skills to diagnose and prevent potential future issues that may be associated with your current injury or presentation.
- Surgery is more effective than Physical Therapy (or “surgery is my only option”)
False. There are many cases in which physical therapy can restore function and reduce pain without surgery. There is new research coming out everyday that shows many pathologies, such as partial rotator cuff tears and meniscal tears, often have the same outcomes whether surgery and physical therapy is performed or physical therapy alone. According to the new information, conservative options such as physical therapy should be tried prior to other more invasive means such as surgery.
- Physical therapy is painful
False. Doctor’s of Physical Therapy play a crucial role in helping those with acute and chronic pain to become pain-free. They work within your pain threshold to achieve the level of function you desire. While a minimal amount of pain can be a part of the rehab process, causing moderate-severe pain with physical therapy can be counter production. Only a very minimal amount of pain shoulder be anticipated with physical therapy.
- I can do physical therapy on my own
False. While you can perform many of the exercises from physical therapy on your own, it is initially important to have guidance in regard to appropriate form and dosage of each exercise. Without appropriate supervision and guidance you will be at increased risk for injury and are not likely to gain optimum results.
Physical Therapy
COMMENTS: 18 Comments
 28 Apr 2017
28 Apr 2017
What Is Physical Therapy
News
COMMENTS: 4 Comments
 28 Apr 2017
28 Apr 2017
Physical Therapy for Foot and Ankle
Read more
Massage Therapy
COMMENTS: 7 Comments
 01 Apr 2017
01 Apr 2017
Sports Medicine of Pearland & Manvel
What is Sports Medicine and Who Can Benefit From it?
- Sports medicine, sometimes referred to as sports science, is a branch of medicine geared towards preventing and treating injuries caused by sports or physical activity. Professional athletes as well as individuals who play sports or exercise recreationally can benefit from sports medicine for diagnostic, curative, rehabilitative, and preventative services.
- Individuals who may potentially benefit from sports medicine includes those wanting to participate in various activities such as going for a walk around the block, a swim, returning to soccer practice, or even attending a ballroom dancing class. You do not have to be a competitive athlete to benefit from sports medicine in helping you regain function and return to the physical activity of your choice.
- Doctors or Physical Therapy (DPT) are able to administer Sports Medicine Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation. Live to Move Physical Therapy in Pearland and Manvel area is equipped with the knowledge to not only heal you to normal function, but adequately prepare you for the activity you wish to return to. We also have DPTs on staff who are Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialists if you desire to continue your health and fitness journey after your therapy with our strength and conditioning classes!
Massage Therapy / Physical Therapy
COMMENTS: 1 Comment
 01 Apr 2017
01 Apr 2017
Low Back Pain?
Here are a Few Reasons Why Physical Therapy Should be Your First Choice!
Did you know approximately 60-80% of the population will experience non-specific low back pain at some point in their lives?? This is the majority of people, making low back pain extremely prevalent around the world. Although many risk factors have been identified including occupational posture, depressive moods, obesity, body height, and age, the cause of low back pain remains obscure making diagnosis difficult.
News
COMMENTS: No Comments
